Biology STAAR EOC BIOLOGY STUDY GUIDE KEY
MAY 8TH IS THE BIOLOGY STAAR EOC TEST
Hypothesis is an educated guess that can be tested. A theory has been tested by scientists hundreds of times and has given rise to the same results/data
10% of energy is transferred 100 à 10 à 1 à .1 à .01
The arrow represents the direction in which the energy flows/ is eaten by
The grass is eaten by the mouse, the mouse is eaten by the snake, etc.
Producers would be located on the bottom in the largest trophic level
The carrying capacity is affected by the number of organisms, the amount of food, space & mates available for the organisms, if a new predator has been introduced to the ecosystem, natural disasters (flooding, drought, fire, tornando)
Bacteria are the only organisms on earth that can transfer the nitrogen in the atmosphere into a useable form for other organisms (such as animals) to use
Secondary succession occurs after the first climax community has already been established. It will only occur if the first community has been destroyed by a natural disaster (fire, drought, flood)
Lichens, algae, and fungi
A community with plants and animals that are stable and in balance
monosaccharide
lipid
Nucleic acids
Proteins
carbohydrates
Starch – it turns purpleish black
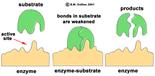
Denatures – it will unfold and no longer be functional
Speeds up chemical processes
To the active site on the enzyme
unfold
It is the smallest functional unit
Robert Hooke was the first person to view cells under a microscope, he observed cork and noticed that it looked like little boxes
Prokaryotic has no true nucleus or no membrane bound organelles. Eukaryotic has a true nucleus and membrane bound organelles
Cell wall, chloroplast, central vacuole
particles move from an area of high concentration to low concentration
Water moves across a membrane
Phospholipid bilayer – heads are hydrophilic (water loving) and point outward and tails are hydrophobic (water fearing) point inward
An internal and external balance, everything is working correctly
It will allow certain things to flow through the membrane while others need either help or need to go through certain protein channels
Passive transport does not require energy
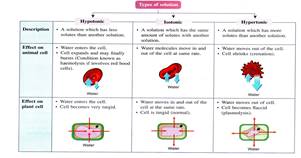
Separation of the cell membrane from the cell wall due to the loss of water
6CO2 + 6H20 + light à C6H12O6 + 6O2
Light energizes electron in carbon dioxide & water in the chloroplast to help produce glucose and oxygen as a waste produce
Chloroplast
Converts the energy from the light into chemical energy. Light is needed for this reaction to occur. The water is split in to Hydrogen ions and Oxygen is released as waste
Light is not needed for this reaction to occur. Makes sugar from the Carbon dioxide and the Hydrogen ions.
Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm
Krebs cycle & Electron Transport Chain occur in the Mitochondria
The exact same thing just in reverse
Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm
Krebs cycle & Electron Transport Chain occur in the Mitochondria
Lots of NADH is produced, this will help run the electron transport chain
DNA and RNA
Sugar, phosphate and a nitrogenous base
Rosalind Franklin took an X-Ray image of DNA in 1952, James Watson & Francis Crick presented a paper in 1953 that described the structure of the DNA helix.
Adenine - Thymine
Cytosine - Guanine
In order for the cell to go through mitosis the DNA must also replicate. Each new cell will get the same exact genetic information.
|
Bases |
Sugar |
Location |
Types |
DNA |
A, T, G, C |
deoxyribose |
Nucleus |
All your cells have the same DNA |
RNA |
A, U, G, C |
ribose |
Nucleus & cytoplasm |
mRNA |
A copy of mRNA is created from DNA. There will be no T on mRNA so it will exchange with Uracil. DNA will unzip is small sections and the free nucleotides will match up with complementary base pairs. When the section of mRNA is built it will release from the DNA strand and travel out of the nucleus to a ribosome to create a protein.
The mRNA goes to a ribosome where it will be read. The codon (bases in a row on mRNA) matches up to the tRNA’s anticodon. The tRNA will bring the matching amino acid for the codon. The Amino Acids will then connect by a polypeptide bond. When the sequence has been completed the AA will fold up creating a protein.
Interphase: G1, Synthesis (S), G2
Mitosis: Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase
Cytokinesis
During the Synthesis phase when DNA is replicating
Metaphase – middle of the cell
Prophase
Anaphase - apart
46 chromosomes
Body cells that do not contain x or y chromosomes
Mitosis is the division or creation of new cells, which supports the theory that all cells come from pre-existing cells
The karyotype is a map of the unborn child’s chromosomes. It will show if there is a trisomy or a deletion of a chromosome
In Animal cells: The cytoplasm divides pinching inward creating a cleavage and forming 2 new cells
In Plant cells: a cell plate forms in the middle of the cell and then the cell wall forms dividing the new plant cells.
The tumor suppressor gene is not turned off so the cells continue to divide uncontrolled
100% of your DNA is the same in each of your cells
Genes are turned on or off
Exposure to different things, radiation, foods, drugs, perscriptions
Activated or deactivated certain genes
Cells that are only for egg or sperm
4 daughter cells that are not identical
Exchange of genetic material during prophase 1, this allows for genetic diversity
Metaphase 1
Telophase 2
|
Mitosis |
Meiosis |
In what type of cell does the division take place? |
somatic |
gametes |
How many divisions are there? |
1 |
2 |
How many daughter cells are produced? |
2 |
4 |
How many chromosomes are produced? |
46 |
23 |
Are the daughter cells identical or different to the parent cell? |
identical |
different |
Does crossing over occur? |
NO |
YES |
B = brown eyes b = blue eyes
A heterozygous father has children with a homozygous recessive mother.
Bb x bb
Genotypes:
2Bb and 2bb
Phenotypes:
2 blue eyes and 2 brown eyes
B = brown eyes b = blue eyes
A heterozygous father has children with a heterozygous mother.
Bb x Bb
Genotypes:
1BB, 2Bb, 1bb
Phenotypes:
3 Brown Eyes, 1 Blue eye
RR = Red flower WW = White Flower RW = Pink
RR is crossed with WW
How many of the offspring will be RW (pink)?
100%
BB = Blue feather WW = White Feather BW = Blue with white tipped
feathers
BW x BW How many have Blue feathers?25%
How many have White feathers? 25%
How many have Blue with white tipped feathers? 50%
No, should come out to be 25% AA, 50% AB and 25% BB
His studies of natural selection helped create the theory of evolution
Homologous structures have the same basic structure (skeleton) but have different functions. This shows that organisms may have evolved from a common ancestor
The population will adapt.
Camouflage
The islands contained such diverse animals on each island.
Analogous structures
All vertebrates start off very similar as an embryo
Domain à Kingdom à Phylum à Class à Order à Family à Genus à species
Uses Latin or Greek it is a 2 word naming system that uses the Genus and species
classification
Archaeabacteria, Eubacteria, Animalia, Plantea, Protista, Fungi
Fungus
Archaea
Protista
Animalia
Eubacteria
Always start with the first set of instructions and read both sets of instructions and either name it or go to the next set of instructions
Viruses can not replicate on their own. They need a host cell.
Capsid and nucleic acid
Antibiotics will only work on bacterial infections. They inhibit the cell wall from forming when the bacterial cell divides. A virus does not replicate on its own and does not have a cell wall.
1) Virus attaches to the cell wall 2) Virus injects its DNA into the cell 3) Cell reads the DNA and assembles the viral parts 4) Newly assembled viruses will burst out of the cell destroying the cell
In the lysogenic cycle the virus will inject its DNA into the cell, the viral DNA will become a part of the cell’s DNA. The viral DNA will get replicated as the cell go through DNA Replication. Each time the cell divides the viral DNA goes with it. It will lay dormant until the conditions are right and it will then enter into the Lytic Cycle.
Yes, this makes it harder to create vaccines
Yes, will only infect certain cells
Bacillius – rod Coccus – sphere Spirillium – spiral
- Break down dead organisms and recycle the nutrients back into the ecosystem
- Nitrogen Fixation: turn nitrogen into a useable form
Binary fission, cells divide; asexual
Conjugation: exchange of genetic information; sexual
conifers, cycads, Ginkgo, and Gnetales
Pine, cedar, redwood
Produce naked seeds
Any flowering plant, grass
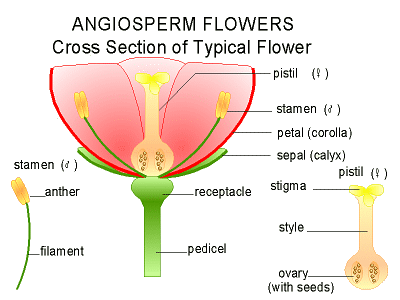
Fertilization occurs inside the female carpel (pistol) Pollen sticks to the stigma, then travels down the style to the ovary. The pollen and ovule then produce a seed(s)
Xylem carries water and phloem carries nutrients
Adaptation that allows the plant to survive
Wind, water, birds, bees, animals eat them then pass the seeds out, animals bury them
Pollination of gymnosperms occurs on the surface of the reproductive organs while it occurs inside of the ovary of the angiosperm
Source: http://www.decaturisd.us/cms/lib3/TX01000649/Centricity/Domain/96/Biology%20STAAR%20EOC%20BIOLOGY%20STUDY%20GUIDE%20KEY.docx
Web site to visit: http://www.decaturisd.us
Author of the text: not indicated on the source document of the above text
If you are the author of the text above and you not agree to share your knowledge for teaching, research, scholarship (for fair use as indicated in the United States copyrigh low) please send us an e-mail and we will remove your text quickly. Fair use is a limitation and exception to the exclusive right granted by copyright law to the author of a creative work. In United States copyright law, fair use is a doctrine that permits limited use of copyrighted material without acquiring permission from the rights holders. Examples of fair use include commentary, search engines, criticism, news reporting, research, teaching, library archiving and scholarship. It provides for the legal, unlicensed citation or incorporation of copyrighted material in another author's work under a four-factor balancing test. (source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fair_use)
The information of medicine and health contained in the site are of a general nature and purpose which is purely informative and for this reason may not replace in any case, the council of a doctor or a qualified entity legally to the profession.
The following texts are the property of their respective authors and we thank them for giving us the opportunity to share for free to students, teachers and users of the Web their texts will used only for illustrative educational and scientific purposes only.
All the information in our site are given for nonprofit educational purposes
The information of medicine and health contained in the site are of a general nature and purpose which is purely informative and for this reason may not replace in any case, the council of a doctor or a qualified entity legally to the profession.
www.riassuntini.com